OSTEP:TLB缓存命中和非命中的开销差距
第十九章:实际操作系统的TLB表项
本章为测量实验,主要要求为写一份tlb.c来测试在TLB miss和TLB hit的情况下性能开销的变化,以感受TLB的重要性
对于题中问题的回答
由于
gettimeofday()的函数只能精确到微秒,不足以测试较为精确的时间,因此使用CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID和clock_gettime();搭配即可获得纳秒级的时间测量,具体代码实现如下具体代码实现如下
tlb.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 将进程锁定在某个固定CPU上
void lockCpu(int cpuId)
{
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(cpuId, &mask);
if (sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask) < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "set thread affinity failed\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: ./tlb pages trials");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 将进程锁定在CPU0上
lockCpu(0);
// 申请页的数量
int page_numebr = atoi(argv[1]);
int trials = atoi(argv[2]);
if (page_numebr <= 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Invaild Input");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int jump = sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE) / sizeof(int);
struct timespec start, end;
struct timespec start_hit, end_hit;
int sum_miss = 0;
int sum_hit = 0;
int cnt = 0;
while (trials--)
{
for (int step = 0; step < page_numebr * jump; step += jump)
{
cnt++;
int *array = calloc(page_numebr, getpagesize());
// 计算TLB miss的时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &start);
array[step] += 0;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &end);
sum_miss += end.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec;
// 计算TLB hit的时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &start_hit);
array[step + 1] += 0;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &end_hit);
sum_hit += end_hit.tv_nsec - start_hit.tv_nsec;
free(array);
}
}
int miss_average = sum_miss / cnt;
int hit_average = sum_hit / cnt;
printf("Time per access(TLS miss): %d\n", miss_average);
printf("Time per access(TLS hit): %d\n", hit_average);
return 0;
}该程序主要思路为
- 统计访问内存需要的总时间
- 首先统计
TLB miss的情况,在miss之后TLB被激活 - 统计对应分页内存的后一位,此时
TLB hit,能够成功快速定位 - 将总时间除以操作的总次数,得到最后的平均每次时间(单位为
ns)
大致结果如下
1
2
3> ./tlb 1000 10
Time per access(TLS miss): 2105
Time per access(TLS hit): 223可以明显发现未命中的时候访问时间要远高于
TLB hit时的时间通过
Python对tlb进行调用,大致结果为4.的效果统计结果如下
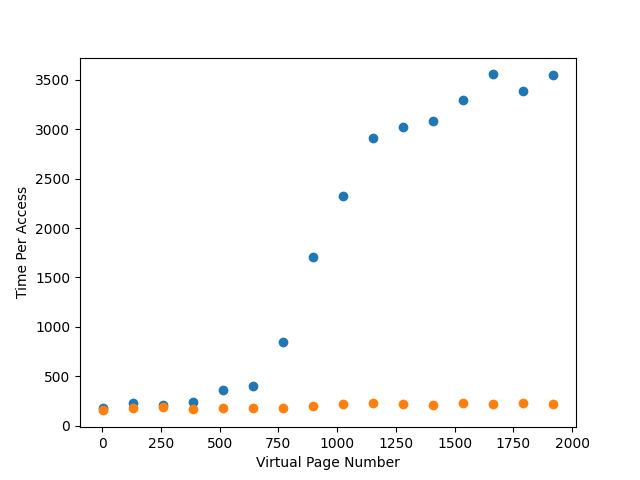
其中蓝色对应
TLB miss的时间,橙色对应了TLB hit的开销时间Python画图代码如下
Matplotlib
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37import os
import sys
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def execRelocation(page_number, trival):
r = os.popen(
'./tlb %d %d' % (page_number, trival))
text = r.read()
pattern = r"(\d+)"
tlb = re.findall(pattern, text)
r.close()
return tlb
page_number = sys.argv[1]
trival = sys.argv[2]
hit_time_access = []
miss_time_access = []
vpn_n = []
for vpn in range(1, int(page_number), 128):
print(str(vpn) + "/" + str(page_number))
tlb = execRelocation(vpn, int(trival))
hit_time_access.append(int(tlb[0]))
miss_time_access.append(int(tlb[1]))
vpn_n.append(vpn)
plt.xlabel("Virtual Page Number")
plt.ylabel("Time Per Access")
plt.scatter(vpn_n, hit_time_access, label="Hit")
plt.scatter(vpn_n, miss_time_access, label="Miss")
plt.savefig("./paging.png")添加
-O0的参数可以防止gcc在编译的时候不进行优化示例如下
1
gcc -O0 tlb.c -o tlb在上下文切换时,解决方案为使用
Docker创建一个单核的虚拟机来进行实验操作,这次实验中,使用sched_setaffinity函数来设置进程对CPU亲和力,以让程序在某一单一CPU上运行。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 将进程锁定在某个固定CPU上
void lockCpu(int cpuId)
{
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(cpuId, &mask);
if (sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask) < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "set thread affinity failed\n");
}
}通过使用
calloc()函数,可以在对堆内的变量进行分配内存的同时进行初始化操作,并且在每一次循环进行之前都销毁数组重新创建,可以减少对实验测试的影响
OSTEP:TLB缓存命中和非命中的开销差距
https://halc.top/p/20416971